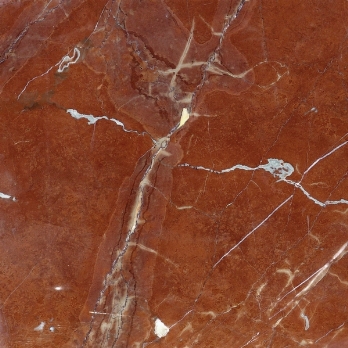
Rosso Collemandina Exclusive
Petrografic name (according EN 12407): Brecciated dolomitic limestone
Macroscopic description: A compact lithotype with a nodular appearance that is dark ruby red in colour with close stylolitic joints that are dark red and in places skin pink or grey. White veins occur that are submillimetric in thickness.
Technical data provides a frame of reference only. As stone is a product of nature, up to date testing to determine specific physical qualities should be repeated for each major project. We decline any responsability for the mis-use of this data, since said data is sourced from the quarry.
Physical mechanical characteristics
| STANDARD | U.M. | MEAN VALUE | ST. DEV. | |
 EN 13755-08 EN 13755-08 |
Water absorption at atmospheric pressure | % | 0,08 | 0,04 |
 EN 1936-07 EN 1936-07 |
Apparent Density | KG/m3 | 2700 | 5,2 |
 EN 1936-07 EN 1936-07 |
Open porosity | % | 0,2 | 0,14 |
 EN 12372-07 EN 12372-07 |
Flexural strength | |||
| (in natural conditions) | MPa | 17,3 | 5,5 | |
| (EN 12371-03 exposed to 48 frost cycles | MPa | 16,9 | 8 | |
 EN 1926-07 EN 1926-07 |
Uniaxial compressive strength | MPa | 94 | 40,9 |
 EN 14231-04 EN 14231-04 |
Slip resistance (honed finishing) | |||
| (dry) | USRV | 62 | 3,2 | |
| (wet) | USRV | 30 | 3,1 | |
Block and slab characteristics
Average size of blocks: 2,50 x 1,40 x 1,40m.
Slabs are preferably cut against the grain or perpendicular to the grain, i.e. the hard way or the easy way.
 Cutting of blocks
Cutting of blocks  Surface lavoration
Surface lavoration
 Cutting of blocks
Cutting of blocks  Surface lavoration
Surface lavoration
Microscopic description according to EN 12407 e EN 12460
| A brecciated sedimentary lithotype in a neomorphism and dolomitization condition. The material is composed of clasts, the dimensions of which vary from mm to dm, composed of micrite with widespread dolomitic crystals. The micrite is partly spotted by hematic microgranulations that generate areas of a deep red colour. Immersed inside are recrystallised bioclasts including foraminifera, fragments of crinoids and bivalves together with relicts of bioclasts that cannot be determined. There are both fractures calcitized from sedimentary rocks and in places fractures recemented by dolomite, calcite and hematic opaque minerals. The clasts are immersed in a macrocristalline calcitic and dolomitic cement (< 300 µm) associated with intrabasinal lithoclasts with abundant fragments of bioclasts and granulations of hematite and limonite. |